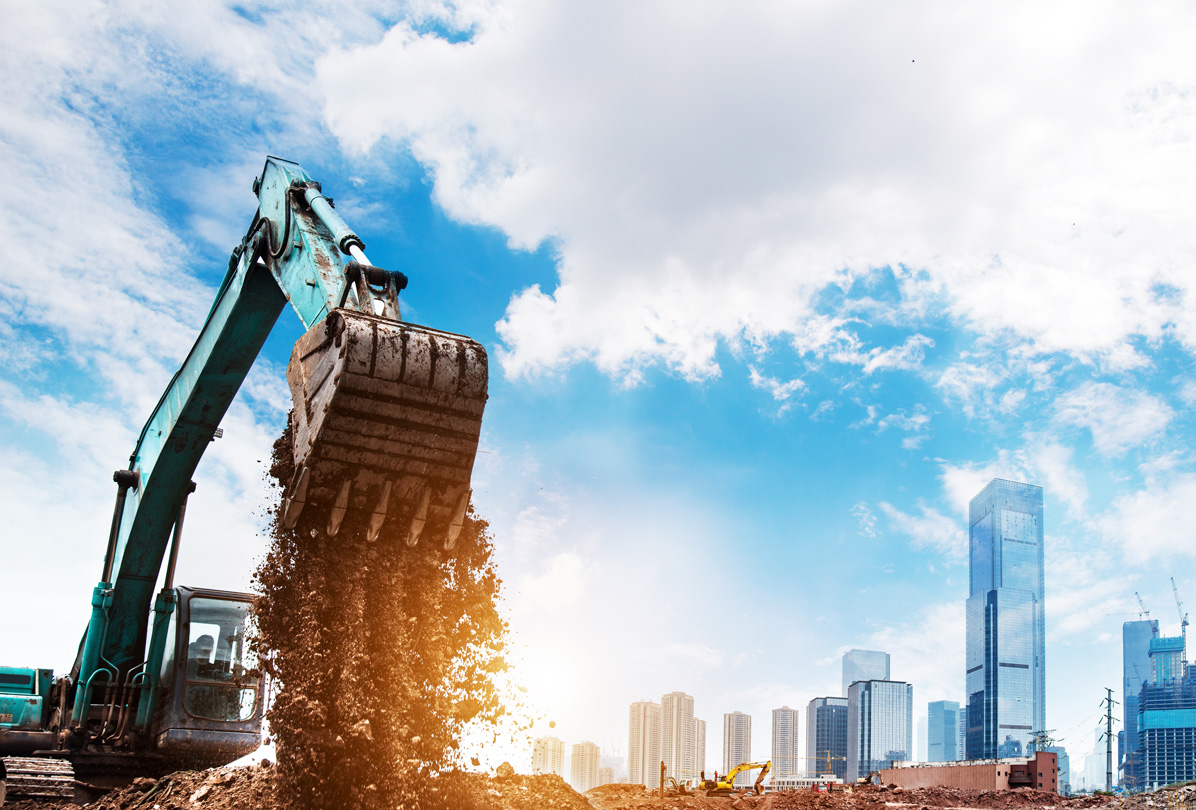
Excavation is a critical phase in the construction process, and it involves the removal of earth, rock, and other materials to create space for foundations, utilities, basements, or other construction elements. Proper excavation is essential for ensuring the stability and safety of a construction site. Here’s an overview of the process of excavating construction sites:
- Site Preparation: Before excavation begins, the construction site is prepared. This includes clearing the area of vegetation, debris, and any structures that need to be demolished. Site boundaries and excavation areas are marked.
- Surveying and Marking: Professional surveyors are often involved to precisely mark the excavation boundaries and levels. This helps ensure that the excavation is done to the correct dimensions and at the required depth.
- Safety Measures: Safety is paramount in excavation. The site should be properly secured with barriers and signage to prevent unauthorized access. Excavation workers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and be trained in safety protocols.
- Selection of Equipment: The choice of excavation equipment depends on the type of soil, depth, and scope of the excavation. Common equipment includes excavators, backhoes, bulldozers, and trenchers. The selection of the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and safety.
- Cutting and Removal: The excavation process begins with cutting into the ground surface to remove the topsoil and subsoil layers. This may involve digging trenches, pits, or creating slopes as required by the construction plans. The excavated material is stockpiled or transported off-site.
- Shoring and Bracing: In deep excavations, especially for foundations or basements, shoring and bracing systems may be necessary to prevent soil collapse or cave-ins. These systems provide support to the surrounding soil during excavation.
- Utility Identification: Before excavation, it’s essential to identify and mark the locations of underground utilities such as water pipes, gas lines, electrical cables, and sewer systems. This helps prevent accidental damage during excavation.
- Excavation to Design Levels: The excavation continues, gradually reaching the desired depth and shape as specified in the construction plans. The process is closely monitored to ensure accuracy.
- Dewatering: In areas with a high water table, dewatering may be necessary to remove excess groundwater from the excavation site. This prevents flooding and maintains a dry working environment.
- Soil Testing: Throughout the excavation process, soil samples may be taken and tested to assess soil quality and ensure it meets construction requirements. This information can guide any necessary soil stabilization measures.
- Backfilling: After the construction work in the excavation is complete (such as installing foundations, utilities, or basements), the excavated area is backfilled with suitable materials and compacted to ensure stability.
- Site Cleanup: Once the excavation is finished, the site is cleaned up, and any excess soil or debris is removed. Proper site cleanup is crucial for the safety of workers and the surrounding environment.
Excavation is a complex and highly specialized aspect of construction, and it’s essential to hire experienced contractors who understand the intricacies of the process and adhere to safety regulations. Additionally, all excavation work should be carried out in compliance with local building codes and regulations.